What's New in Go 1.24?
Go 1.24 is shaping up to be a significant release, introducing a range of enhancements focused on performance, security, and developer experience. These changes aim to make Go even more powerful and efficient for building modern applications.
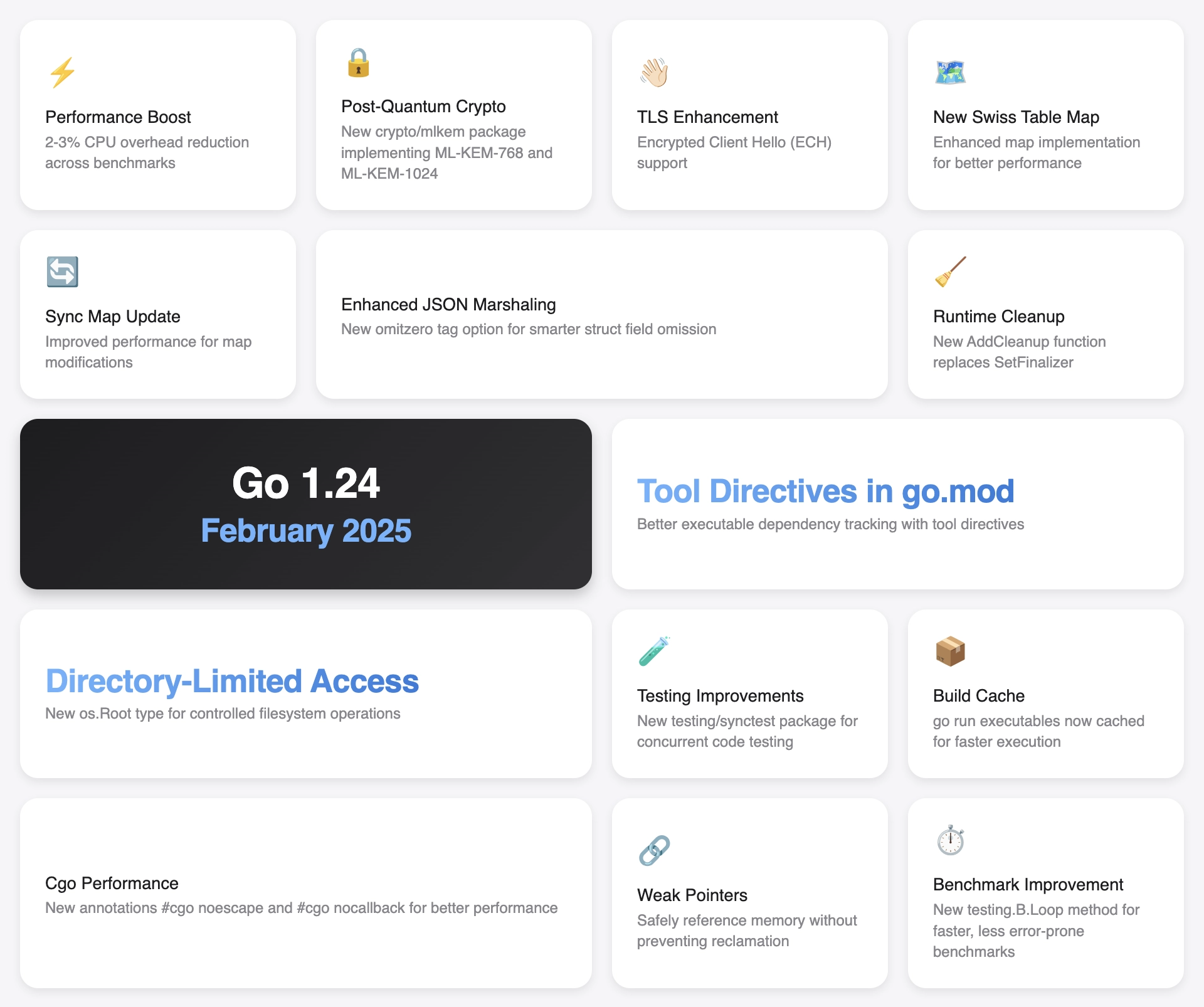
Performance Boost
A general performance improvement with a 2-3% reduction in CPU overhead across a suite of representative benchmarks. These improvements include a new built-in map implementation, more efficient memory allocation of small objects, and a new runtime-internal mutex implementation. Results may vary by application.
Post-Quantum Crypto
Introduction of the crypto/mlkem package, implementing ML-KEM-768 and ML-KEM-1024. ML-KEM is a post-quantum key exchange mechanism formerly known as Kyber and specified in FIPS 203. This addition prepares Go for the future of cryptographic security.
TLS Enhancement
Support for Encrypted Client Hello (ECH) in TLS. This feature can be enabled by populating the Config.EncryptedClientHelloKeys field, enhancing privacy and security for TLS connections.
New Swiss Table Map
An enhanced map implementation for better performance. This new implementation is based on Swiss Tables, and can be disabled with the GOEXPERIMENT=noswissmap build flag.
Sync Map Update
Improved performance for map modifications in sync.Map. Modifications of disjoint sets of keys are much less likely to contend on larger maps, and there is no longer any ramp-up time required to achieve low-contention loads from the map. If you encounter issues, you can revert to the old implementation using GOEXPERIMENT=nosynchashtriemap.
Enhanced JSON Marshaling
A new omitempty tag option for smarter struct field omission during JSON marshaling. When marshaling, a struct field with the omitempty option will be omitted if its value is zero. If the field type has an IsZero() bool method, that will be used to determine whether the value is zero.
Runtime Cleanup
Introduction of AddCleanup function to replace SetFinalizer for better resource management. Unlike SetFinalizer, it does not resurrect the object it is attached to for finalization, and multiple cleanups may be attached to a single object. New code should prefer AddCleanup over SetFinalizer.
Tool Directives in go.mod
Improved executable dependency tracking using tool directives in go.mod. This removes the need for the previous workaround of adding tools as blank imports to a file conventionally named “tools.go”.
Directory-Limited Access
New os.Root type for controlled filesystem operations. The os.Root type provides the ability to perform filesystem operations within a specific directory, preventing access outside of the specified path.
Testing Improvements
New testing/synctest package for testing concurrent code. The synctest.Run function starts a group of goroutines in an isolated “bubble”, and synctest.Wait function waits for all goroutines in the current bubble to block. This package is experimental and must be enabled by setting GOEXPERIMENT=synctest at build time.
Build Cache
go run executables are now cached for faster execution. This makes repeated executions faster at the expense of making the cache larger.
Cgo Performance
New #cgo noescape and #cgo nocallback annotations for better Cgo performance. #cgo noescape cFunctionName tells the compiler that memory passed to the C function does not escape. #cgo nocallback cFunctionName tells the compiler that the C function does not call back to any Go functions.
Weak Pointers
Support for weak pointers to safely reference memory without preventing reclamation. Weak pointers are a low-level primitive provided to enable the creation of memory-efficient structures, such as weak maps for associating values, canonicalizations maps, and various kinds of caches.
Benchmark Improvement
New testing.B.Loop method for faster, less error-prone benchmarks. The benchmark function will execute exactly once per -count, so expensive setup and cleanup steps execute only once. Function call parameters and results are kept alive, preventing the compiler from fully optimizing away the loop body.
Go 1.24 is shaping up to be a significant release, offering substantial improvements in various aspects of the language and its ecosystem.