通过 Redis 客户端侧缓存提升响应能力
What is Redis?
레디스를 모르는 분은 별로 없을 거라 생각합니다. 하지만 그래도 몇가지 특성으로 짧게 언급하고 넘어가자면 다음과 같이 정리할 수 있을 것입니다.
- 단일 스레드에서 연산이 수행되어, 모든 연산이 원자성을 가집니다.
- In-Memory에 데이터가 저장되고 연산되어, 모든 연산이 빠릅니다.
- 레디스는 옵션에 따라 WAL을 저장할 수 있어, 빠르게 최신 상태를 백업하고 복구할 수 있습니다.
- Set, Hash, Bit, List 등의 여러가지 타입을 지원하여, 높은 생산성을 가집니다.
- 큰 커뮤니티를 가지고 있어, 다양한 경험과 이슈, 해결법을 공유받을 수 있습니다.
- 오랫동안 개발 및 운영되어, 신뢰할 수 있는 안정성이 있습니다.
그래서 본론으로
상상해보세요?
만약 여러분들의 서비스의 캐시가 다음 두가지 조건에 부합한다면 어떨까요?
- 자주 조회되는 데이터를 최신 상태로 사용자에게 제공해야하지만, 갱신이 불규칙하여 캐시 갱신을 빈번하게 해야할 때
- 갱신은 안되지만, 동일한 캐시 데이터에 자주 접근해서 조회해야할 때
첫번째 케이스는 쇼핑몰 실시간 인기 순위를 고려할 수 있습니다. 쇼핑몰 실시간 인기 순위를 sorted set으로 저장했을 때, 레디스에서 사용자가 메인 페이지에 접근할 때마다 읽으면 비효율적입니다.
두번째 케이스는 환율 데이터에 대해, 대략적으로 10분 주기로 환율 데이터가 고시되어도 실제 조회는 매우 빈번하게 발생합니다. 그것도 원-달러, 원-엔, 원-위안에 대해서는 매우 빈번하게 캐시를 조회하게 됩니다.
이러한 케이스들에서는 API 서버가 로컬에 별도의 캐시를 가지고 있다가, 데이터가 변경되면 레디스를 다시 조회해서 갱신하는 편이 효율적인 동작일 것입니다.
그러면 어떻게 하면 데이터베이스 - 레디스 - API 서버 구조에서 이러한 동작을 구현할 수 있을까요??
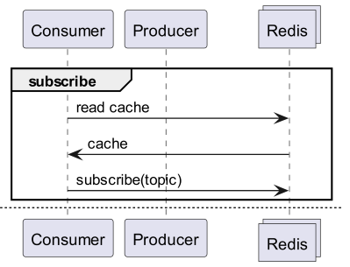
Redis PubSub으로 안되나?
캐시를 사용할 때, 갱신 여부를 받을 수 있는 채널을 구독하자!
- 그럼 갱신 시에 메시지를 전송하는 로직을 만들어야 합니다.
- PubSub으로 인한 추가 동작이 들어가기에 성능에 영향을 줍니다.
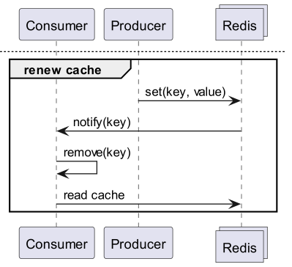
그럼 Redis가 변경을 감지한다면?
Keyspace Notification을 사용하여 해당 키에 대한 커맨드 알림을 받으면?
- 갱신에 쓰이는 키와 커맨드를 미리 저장하고 공유해야하는 번거로움이 존재합니다。
- 예를 들어, 어떤 키에 대해선 단순 Set이 갱신 커맨드고, 어떤 키는 LPush, 혹은 RPush나 SAdd 및 SRem이 갱신 커맨드가 되는 등 복잡해집니다。
- 이는 개발 과정에서 커뮤니케이션 미스와 코딩에서 휴먼 에러를 발생시킬 가능성이 대폭 증가합니다。
Keyevent Notification을 사용하여 커맨드 단위로 알림을 받으면?
- 갱신에 쓰이는 모든 커맨드에 대한 구독이 필요합니다。거기서 들어오는 키에 대해 적절한 필터링이 필요합니다。
- 예를 들어, Del로 들어오는 모든 키 중 일부에 대해 해당 클라이언트는 로컬 캐시가 없을 가능성이 높습니다。
- 이는 불필요한 리소스 낭비로 이어질 수 있습니다。
그래서 필요한 것이 Invalidation Message!
Invalidation Message가 무엇?
Invalidation Messages는 Redis 6.0부터 추가된 Server Assisted Client-Side Cache의 일환으로 제공되는 개념입니다. Invalidation Message는 다음 흐름으로 전달됩니다.
- ClientB가 이미 key를 한번 읽었다고 가정합니다.
- ClientA가 해당 key를 새로 설정합니다.
- Redis는 변경을 감지하고 ClientB에 Invalidation Message를 발행해서 ClientB에 캐시를 지우라고 알립니다.
- ClientB는 해당 메시지를 받아서 적절한 조치를 취합니다.
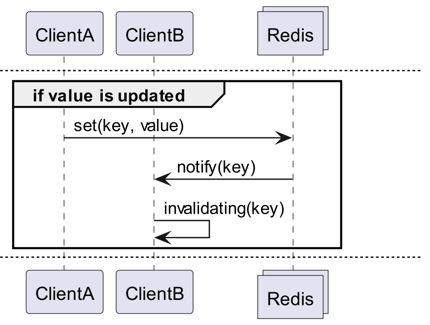
어떻게 쓰는 거지
기본 동작 구조
레디스에 연결된 클라이언트가 CLIENT TRACKING ON REDIRECT <client-id>를 실행함으로 invalidation message를 받도록 합니다. 그리고 메시지를 받아야 하는 클라이언트는 SUBSCRIBE __redis__:invalidate로 invalidation message를 받도록 구독합니다.
default tracking
1# client 1
2> SET a 100
1# client 3
2> CLIENT ID
312
4> SUBSCRIBE __redis__:invalidate
51) "subscribe"
62) "__redis__:invalidate"
73) (integer) 1
1# client 2
2> CLIENT TRACKING ON REDIRECT 12
3> GET a # tracking
1# client 1
2> SET a 200
1# client 3
21) "message"
32) "__redis__:invalidate"
43) 1) "a"
broadcasting tracking
1# client 3
2> CLIENT ID
312
4> SUBSCRIBE __redis__:invalidate
51) "subscribe"
62) "__redis__:invalidate"
73) (integer) 1
1# client 2
2CLIENT TRACKING ON BCAST PREFIX cache: REDIRECT 12
1# client 1
2> SET cache:name "Alice"
3> SET cache:age 26
1# client 3
21) "message"
32) "__redis__:invalidate"
43) 1) "cache:name"
51) "message"
62) "__redis__:invalidate"
73) 1) "cache:age"
구현! 구현! 구현!
Redigo + Ristretto
저렇게만 설명하면 실제로 코드 상에서 사용할 때에 어떻게 써야할지 애매합니다. 그러니 간단하게 redigo와 ristretto로 먼저 구성해 보겠습니다。
먼저 두 디펜던시를 설치합니다.
github.com/gomodule/redigogithub.com/dgraph-io/ristretto
1package main
2
3import (
4 "context"
5 "fmt"
6 "log/slog"
7 "time"
8
9 "github.com/dgraph-io/ristretto"
10 "github.com/gomodule/redigo/redis"
11)
12
13type RedisClient struct {
14 conn redis.Conn
15 cache *ristretto.Cache[string, any]
16 addr string
17}
18
19func NewRedisClient(addr string) (*RedisClient, error) {
20 cache, err := ristretto.NewCache(&ristretto.Config[string, any]{
21 NumCounters: 1e7, // number of keys to track frequency of (10M).
22 MaxCost: 1 << 30, // maximum cost of cache (1GB).
23 BufferItems: 64, // number of keys per Get buffer.
24 })
25 if err != nil {
26 return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to generate cache: %w", err)
27 }
28
29 conn, err := redis.Dial("tcp", addr)
30 if err != nil {
31 return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to connect to redis: %w", err)
32 }
33
34 return &RedisClient{
35 conn: conn,
36 cache: cache,
37 addr: addr,
38 }, nil
39}
40
41func (r *RedisClient) Close() error {
42 err := r.conn.Close()
43 if err != nil {
44 return fmt.Errorf("failed to close redis connection: %w", err)
45 }
46
47 return nil
48}
먼저 간단하게 ristretto와 redigo를 포함하는 RedisClient를 생성합니다。
1func (r *RedisClient) Tracking(ctx context.Context) error {
2 psc, err := redis.Dial("tcp", r.addr)
3 if err != nil {
4 return fmt.Errorf("failed to connect to redis: %w", err)
5 }
6
7 clientId, err := redis.Int64(psc.Do("CLIENT", "ID"))
8 if err != nil {
9 return fmt.Errorf("failed to get client id: %w", err)
10 }
11 slog.Info("client id", "id", clientId)
12
13 subscriptionResult, err := redis.String(r.conn.Do("CLIENT", "TRACKING", "ON", "REDIRECT", clientId))
14 if err != nil {
15 return fmt.Errorf("failed to enable tracking: %w", err)
16 }
17 slog.Info("subscription result", "result", subscriptionResult)
18
19 if err := psc.Send("SUBSCRIBE", "__redis__:invalidate"); err != nil {
20 return fmt.Errorf("failed to subscribe: %w", err)
21 }
22 psc.Flush()
23
24 for {
25 msg, err := psc.Receive()
26 if err != nil {
27 return fmt.Errorf("failed to receive message: %w", err)
28 }
29
30 switch msg := msg.(type) {
31 case redis.Message:
32 slog.Info("received message", "channel", msg.Channel, "data", msg.Data)
33 key := string(msg.Data)
34 r.cache.Del(key)
35 case redis.Subscription:
36 slog.Info("subscription", "kind", msg.Kind, "channel", msg.Channel, "count", msg.Count)
37 case error:
38 return fmt.Errorf("error: %w", msg)
39 case []interface{}:
40 if len(msg) != 3 || string(msg[0].([]byte)) != "message" || string(msg[1].([]byte)) != "__redis__:invalidate" {
41 slog.Warn("unexpected message", "message", msg)
42 continue
43 }
44
45 contents := msg[2].([]interface{})
46 keys := make([]string, len(contents))
47 for i, key := range contents {
48 keys[i] = string(key.([]byte))
49 r.cache.Del(keys[i])
50 }
51 slog.Info("received invalidation message", "keys", keys)
52 default:
53 slog.Warn("unexpected message", "type", fmt.Sprintf("%T", msg))
54 }
55 }
56}
代码稍微有些复杂。
- 为了进行 Tracking,需要额外建立一个连接。这是考虑到 PubSub 可能会干扰其他操作而采取的措施。
- 查询新增连接的 ID,然后让查询数据的连接将 Tracking 重定向到该连接。
- 接着订阅 Invalidation Message。
- 处理订阅的代码稍微复杂。由于 redigo 无法解析失效消息,因此需要接收未解析的响应进行处理。
1func (r *RedisClient) Get(key string) (any, error) {
2 val, found := r.cache.Get(key)
3 if found {
4 switch v := val.(type) {
5 case int64:
6 slog.Info("cache hit", "key", key)
7 return v, nil
8 default:
9 slog.Warn("unexpected type", "type", fmt.Sprintf("%T", v))
10 }
11 }
12 slog.Info("cache miss", "key", key)
13
14 val, err := redis.Int64(r.conn.Do("GET", key))
15 if err != nil {
16 return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to get key: %w", err)
17 }
18
19 r.cache.SetWithTTL(key, val, 1, 10*time.Second)
20 return val, nil
21}
Get 消息会先查询 ristretto,如果不存在,则从 Redis 获取。
1package main
2
3import (
4 "context"
5 "log/slog"
6 "os"
7 "os/signal"
8 "time"
9)
10
11func main() {
12 ctx, cancel := signal.NotifyContext(context.Background(), os.Interrupt)
13 defer cancel()
14
15 client, err := NewRedisClient("localhost:6379")
16 if err != nil {
17 panic(err)
18 }
19 defer client.Close()
20
21 go func() {
22 if err := client.Tracking(ctx); err != nil {
23 slog.Error("failed to track invalidation message", "error", err)
24 }
25 }()
26
27 ticker := time.NewTicker(1 * time.Second)
28 defer ticker.Stop()
29 done := ctx.Done()
30
31 for {
32 select {
33 case <-done:
34 slog.Info("shutting down")
35 return
36 case <-ticker.C:
37 v, err := client.Get("key")
38 if err != nil {
39 slog.Error("failed to get key", "error", err)
40 return
41 }
42 slog.Info("got key", "value", v)
43 }
44 }
45}
用于测试的代码如上所示。您可以尝试测试一下,会发现每次 Redis 中的数据更新时,值都会被刷新。
然而,这过于复杂。最重要的是,为了扩展到集群,不可避免地需要对所有 Master 或 Replica 启用 Tracking。
Rueidis
对于使用 Go 语言的我们来说,有最现代且最先进的 rueidis。我们将编写使用 rueidis 在 Redis 集群环境中实现 Server Assisted Client-Side Cache 的代码。
首先,安装依赖项。
github.com/redis/rueidis
然后,编写查询 Redis 数据的代码。
1package main
2
3import (
4 "context"
5 "log/slog"
6 "os"
7 "os/signal"
8 "time"
9
10 "github.com/redis/rueidis"
11)
12
13func main() {
14 ctx, cancel := signal.NotifyContext(context.Background(), os.Interrupt)
15 defer cancel()
16
17 client, err := rueidis.NewClient(rueidis.ClientOption{
18 InitAddress: []string{"localhost:6379"},
19 })
20 if err != nil {
21 panic(err)
22 }
23
24 ticker := time.NewTicker(1 * time.Second)
25 defer ticker.Stop()
26 done := ctx.Done()
27
28 for {
29 select {
30 case <-done:
31 slog.Info("shutting down")
32 return
33 case <-ticker.C:
34 const key = "key"
35 resp := client.DoCache(ctx, client.B().Get().Key(key).Cache(), 10*time.Second)
36 if resp.Error() != nil {
37 slog.Error("failed to get key", "error", resp.Error())
38 continue
39 }
40 i, err := resp.AsInt64()
41 if err != nil {
42 slog.Error("failed to convert response to int64", "error", err)
43 continue
44 }
45 switch resp.IsCacheHit() {
46 case true:
47 slog.Info("cache hit", "key", key)
48 case false:
49 slog.Info("missed key", "key", key)
50 }
51 slog.Info("got key", "value", i)
52 }
53 }
54}
在 rueidis 中,只需 DoCache 即可使用 Client-Side Cache。它会将数据添加到本地缓存中,并决定在本地缓存中保留多长时间,然后再次调用 DoCache 时,会从本地缓存中查询数据。当然,它也能正常处理失效消息。
为什么不用 redis-go?
redis-go 遗憾的是,它不通过官方 API 支持 Server Assisted Client-Side Cache。甚至在创建 PubSub 时,它会创建新的连接,但没有直接访问该连接的 API,因此也无法知道 Client ID。因此,我们认为 redis-go 的架构本身就不可能实现,所以跳过了。
魅力非凡
通过 Client-Side Cache 架构
- 如果数据可以提前准备,这种架构可以最大限度地减少对 Redis 的查询和流量,并始终提供最新数据。
- 通过这种方式,可以创建一种 CQRS 架构,从而显著提高读取性能。
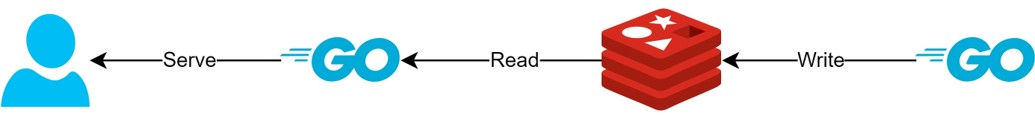
它的魅力何在?
实际上,由于现场正在使用这种架构,我简单地查询了两个 API 的延迟。请原谅我只能非常抽象地描述。
- 第一个 API
- 首次查询时:平均 14.63ms
- 后续查询时:平均 2.82ms
- 平均差距:10.98ms
- 第二个 API
- 首次查询时:平均 14.05ms
- 后续查询时:平均 1.60ms
- 平均差距:11.57ms
延迟最多额外改善了约 82%!
预计会有以下改进:
- 省略客户端和 Redis 之间的网络通信过程,并节省流量。
- 减少 Redis 本身需要执行的读取命令数量。
- 这也具有提高写入性能的效果。
- 最小化 Redis 协议的解析。
- 解析 Redis 协议并非没有成本。减少这一成本是一个巨大的机会。
然而,一切都是权衡。为此,我们至少牺牲了以下两点:
- 客户端 Side Cache 管理组件的实现、操作和维护需求。
- 由此导致的客户端 CPU 和内存使用量增加。
结论
就我个人而言,这是一个令人满意的架构组件,并且对延迟和 API 服务器的压力也非常小。我希望将来如果可能的话,也能以这种结构构建架构。